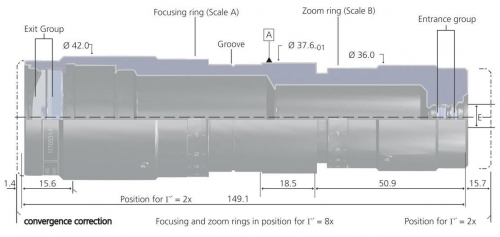
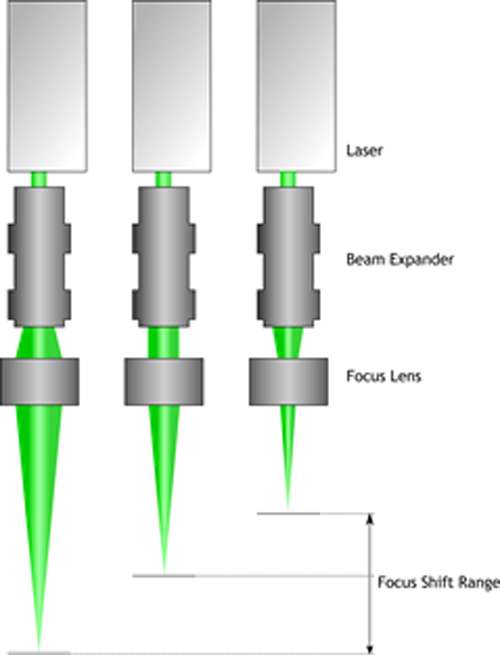
They are ideal for applications in which a small spot must be formed at some distance from the laser or where the collimation range must be extended for illumination or for alignment of distant objects.
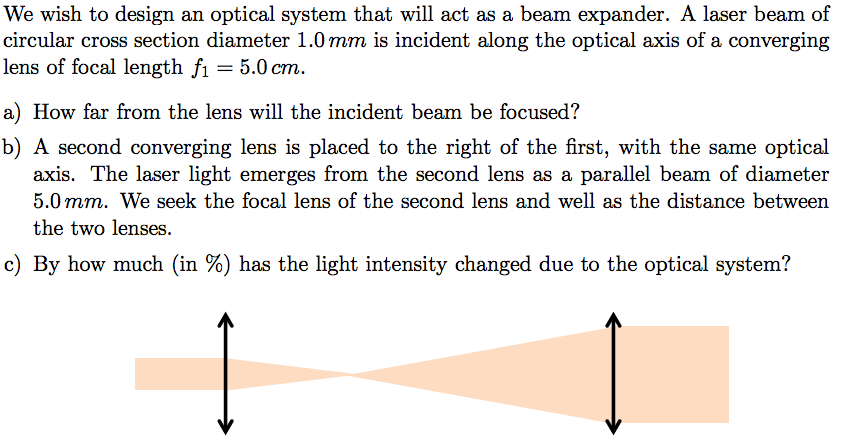
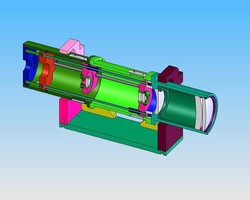
Laser beam expander design.
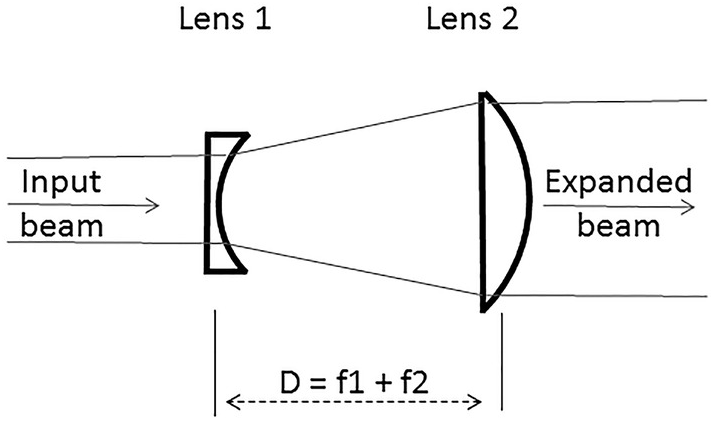
Galilean beam expanders in which an objective lens with a negative focal length and an image lens with a positive focal length are separated by the sum of their focal lengths are simple lower cost designs that also avoid the internal focus of keplerian beam expanders figure 4 the lack of an internal focus makes galilean beam expanders better suited for high power laser applications than.
We also assume the input beam is gaussian and that we are mounting the beam expander directly to the laser simplifying the angle of incidence to 0 degrees.
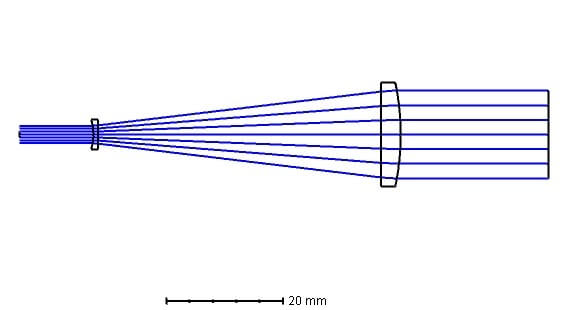
When a collimated laser beam is input to one side of the beam expander a collimated beam is output from the other end that is the object space and image space rays converge at infinity.
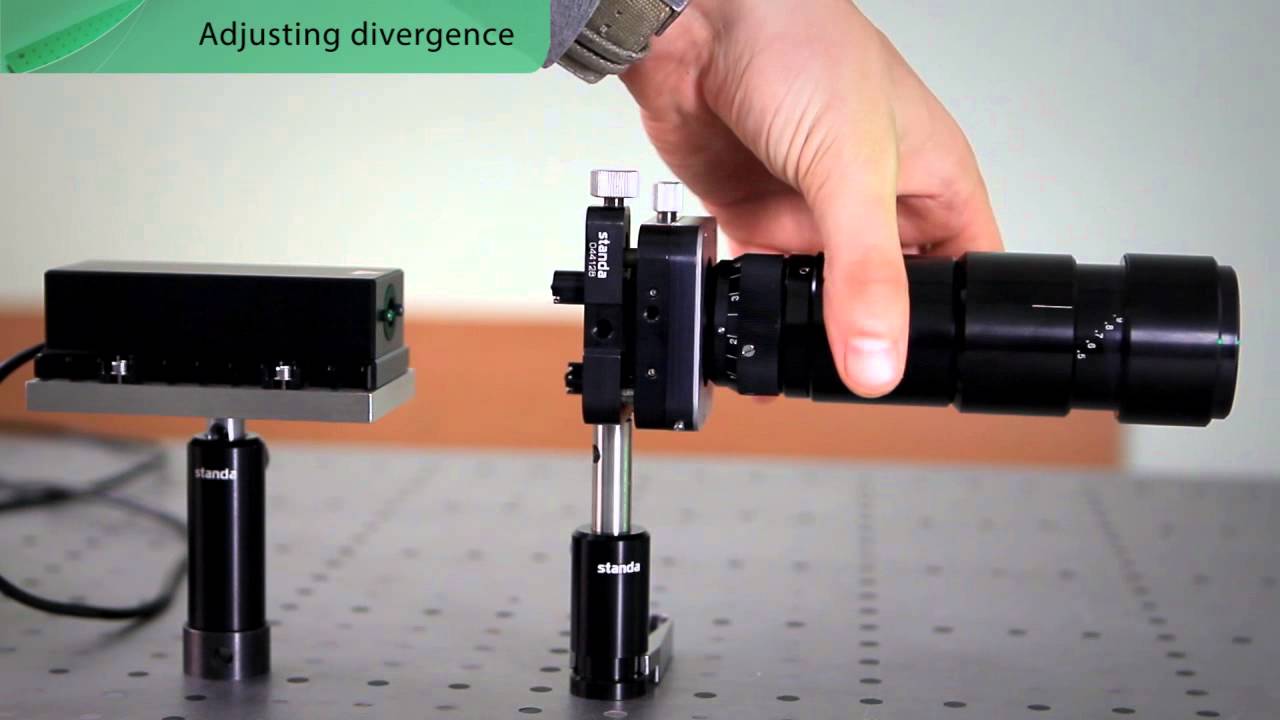
These galilean design beam expanders provide an adjustable focus for collimation at varying wavelengths and to control divergence correction and focusing.
Laser beam expanders are typically of galilean design.
They are adaptable for complex applications requiring increased power density at the focal point beam guidance over long distance dual wavelengths 1064nm and 532nm high power laser.







.jpg)